Have a look at our new research article published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (IF: 6.514), an interdisciplinary collaboration with the research group of Nenad Filipovic (Univ Belgrad, Servia) and with researchers from the University of Gdansk (Poland), Institute Ruder Boskovic (Zagreb, Croatia) and Universidad de La Laguna (Tenerife, Spain).
In this study, we describe the synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of a series of cadmium complexes with thiazolyl/selenazoyl-hydrazone ligands. The activity of these complexes was tested against different types of tumor cell models. The antiproliferative activity study revealed that all complexes are more active compared to 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin, yielding interesting prospects for future developments.
Study of the anticancer potential of Cd complexes of selenazoyl-hydrazones and their sulphur isosters
Sanja B. Marković, Natalia Maciejewska, Mateusz Olszewski, Aleksandar Višnjevac, AdriánPuerta, José M.Padrón, IrenaNovaković, Snežana Kojić, Henrique S. Fernandes, Sérgio F. Sousa, Sandra Ramotowska, Agnieszka Chylewska, Mariusz Makowski, Tamara R.Todorović, and Nenad R.Filipović
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry | DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114449 | Free Download (50 days only)
Abstract
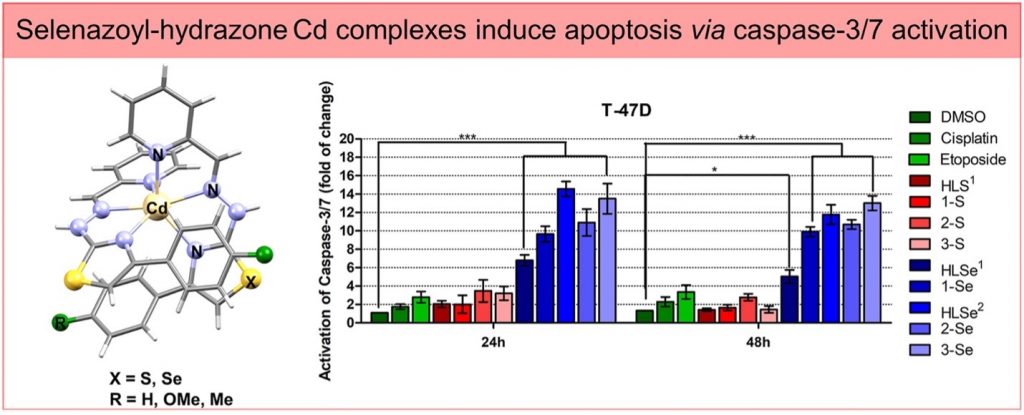
The biological activity of Cd compounds has been investigated scarce since Cd has been recognized as a human carcinogen. However, the toxicity of cadmium is comparable to the toxicity of noble metals such as Pt and Pd. The paradigm of metal toxicity has been challenged suggesting that metal toxicity is not a constant property, yet it depends on many factors like the presence of appropriate ligands. Studies on anticancer activity of cadmium complexes showed that the complexation of various ligands resulted in complexes that showed better activities than approved drugs. In the present study, cadmium complexes with biologically potent thiazolyl/selenazoyl-hydrazone ligands have been prepared, and tested for their activity against different types of tumor cell models. The complexation of ligands with Cd(II) resulted in a synergistic effect. The antiproliferative activity study revealed that all complexes are more active compared to 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. The mechanism of tumor cell growth inhibition reveal that selenium-based compounds induce cell death in T-47D (gland carcinoma) cells through apoptosis via caspase-3/7 activation. Additionally, their pro-apoptotic effect was stronger compared to etoposide and cisplatin. Nuclease activity, detected by gel electrophoresis, may be the possible mechanism of anticancer action of investigated complexes.
