Please, check our recent publication in Current Medicinal Chemistry (IF 4.184):
Multifunctional Enzymes as Targets for the Treatment of Tuberculosis: Paving the Way for New Anti-TB Drugs
Carla S.S. Teixeira, Nuno M. F. S. A. Cerqueira, Sérgio F. Sousa
DOI: 10.2174/0929867328666201229122722 | Current Medicinal Chemistry
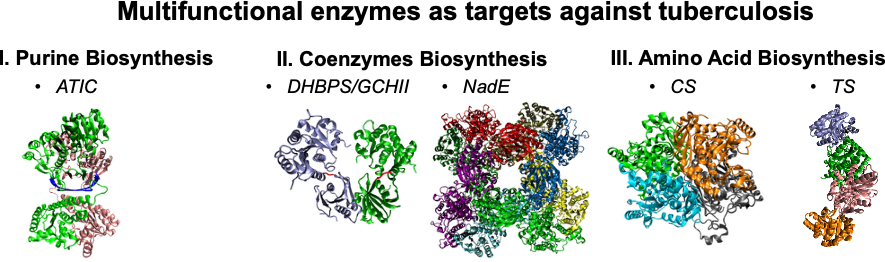
This work summarizes recent developments on anti-Tuberculosis therapy, starting by discussing the current epidemiologic status and presenting an overview of the history of anti-tuberculosis drug discovery. Special attention is dedicated to five multifunctional enzymes that are regarded as promising targets for new anti-TB drugs: 5-aminoimidazole4-carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase/IMP cyclohydrolase (ATIC); 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase (DHBPS)/GTP cyclohydrolase II (GCHII); glutamine dependent NAD+ Synthetase (NadE); chorismate synthase (CS); and Tryptophan synthase (TS). These enzymes are involved in metabolic pathways critical for the M. tuberculosis survival, growth or replication, but that are not expressed in humans or have significant differences in terms of functionality, which makes them appealing targets. Their function, structure, possible catalytic mechanisms and current inhibition strategies and inhibitors are reviewed and discussed.